Post office investments in India offer the public various savings and investment options, providing a secure and accessible means of financial growth as we are heading towards the last quarter of FY 2023-2024. here are the latest post office interest rates.
As the current inflation continues to be high, the government retained all the post office small savings scheme interest rates constant except for the 3-year term Deposit and Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY).

Latest Post Office Interest Rate: Jan-March 2024
Here is the latest post office interest rate comparison:
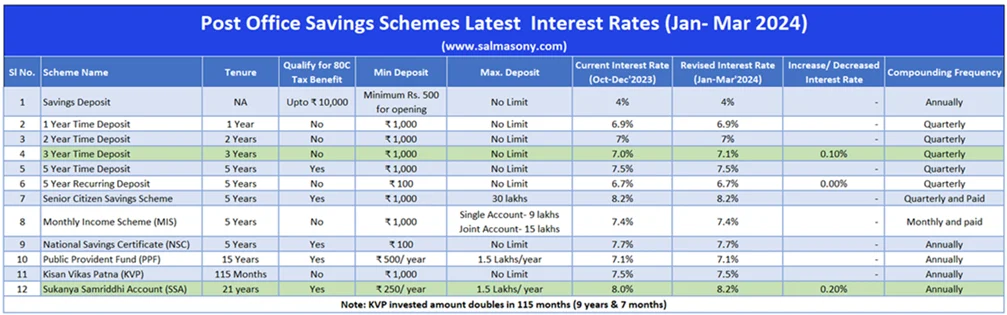
| Post Office Savings Schemes Latest Interest Rates Jan- Mar 2024 (salmasony.com) | |||||||||
| Sl No. | Scheme Name | Tenure | Qualify for 80C Tax Benefit | Min Deposit | Max. Deposit | Current Interest Rate (Oct-Dec’2023) | Revised Interest Rate (Jan-Mar’2024) | Increase/ Decreased Interest Rate | Compounding Frequency |
| 1 | Savings Deposit | NA | Upto ₹ 10,000 | Minimum Rs. 500 for opening | No Limit | 4% | 4% | – | Annually |
| 2 | 1-Year Time Deposit | 1 Year | No | ₹ 1,000 | No Limit | 6.9% | 6.9% | – | Quarterly |
| 3 | 2-Year Time Deposit | 2 Years | No | ₹ 1,000 | No Limit | 7% | 7% | – | Quarterly |
| 4 | 3-Year Time Deposit | 3 Years | No | ₹ 1,000 | No Limit | 7.0% | 7.1% | 0.10% | Quarterly |
| 5 | 5-Year Time Deposit | 5 Years | Yes | ₹ 1,000 | No Limit | 7.5% | 7.5% | – | Quarterly |
| 6 | 5 Year Recurring Deposit | 5 Years | No | ₹ 100 | No Limit | 6.7% | 6.7% | 0.00% | Quarterly |
| 7 | Senior Citizen Savings Scheme | 5 Years | Yes | ₹ 1,000 | 30 lakhs | 8.2% | 8.2% | – | Quarterly and Paid |
| 8 | Monthly Income Scheme (MIS) | 5 Years | No | ₹ 1,000 | Single Account- 9 lakhs Joint Account- 15 lakhs | 7.4% | 7.4% | – | Monthly and paid |
| 9 | National Savings Certificate (NSC) | 5 Years | Yes | ₹ 100 | No Limit | 7.7% | 7.7% | – | Annually |
| 10 | Public Provident Fund (PPF) | 15 Years | Yes | ₹ 500/ year | 1.5 Lakhs/year | 7.1% | 7.1% | – | Annually |
| 11 | Kisan Vikas Patna (KVP) | 115 Months | No | ₹ 1,000 | No Limit | 7.5% | 7.5% | – | Annually |
| 12 | Sukanya Samriddhi Account (SSA) | 21 years | Yes | ₹ 250/ year | 1.5 Lakhs/ year | 8.0% | 8.2% | 0.20% | Annually |
| Note: KVP invested amount doubles in 115 months (9 years & 7 months) | |||||||||
As previously stated, the rates for all other schemes remain unchanged, with the exception of adjustments to the 3-year term Deposit and Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme (SSY). The 3-year term Deposit rate has been raised from 7% to 7.1%. Similarly, the Sukanya Samriddhi Scheme (SSY) rate has increased from 8% to 8.2%. The rates for the remaining schemes will remain unaffected.
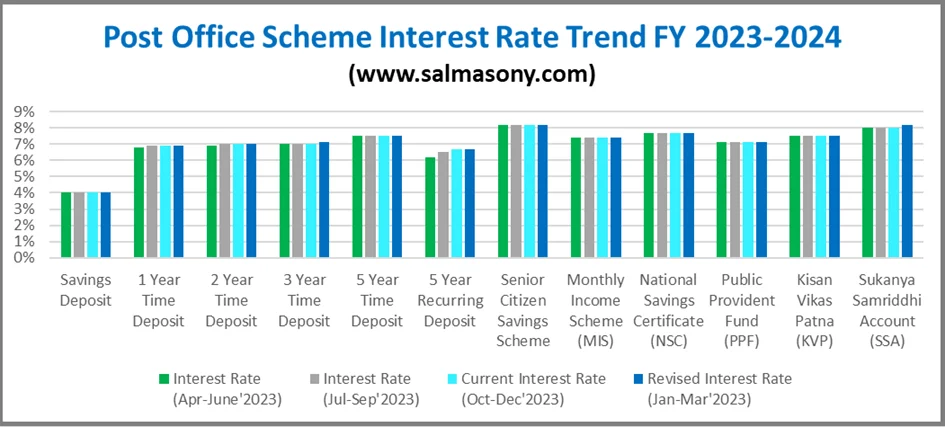
Post Office Interest Rate Trend FY 2023-2024
Let’s look at the trend of Post Office Interest Rate. You will notice the interest rate for the 3-year time deposit, and SSY remains the same for three quarters. Finally, it’s been increased to encourage investment in debt for short-term goals and girls’ education. If you have a girl child, then you must consider SSY as a debt part of the child’s education and marriage goal.
Here is my detailed post on Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana benefits
Popular Post Office Savings Scheme Features
Post offices offer a variety of savings schemes to cater to the diverse financial needs of individuals. Here are some features of popular Post Office Savings Schemes:
1) Post Office Savings Account
A Post Office Savings Account is a basic savings account provided by the postal department in many countries, including India. These accounts are a simple and accessible way for individuals to save money and earn a modest interest on their deposits. The Post Office Savings Account in India is particularly popular due to its widespread reach, making it available to people in both urban and rural areas.
Here are key features and details about the Post Office Savings Account in India:
- Accessibility: Post Office Savings Accounts are widely accessible nationwide, even in remote areas where traditional banking services may be limited.
- Account Type: The Account can be opened as an individual or joint account. Joint accounts can be opened, and up to three adults can be joint account holders. Minor individuals can also open an account with a guardian.
- Interest Rates: The government sets the interest rates on Post Office Savings Accounts, which are subject to quarterly revisions. Interest is compounded annually and credited to the Account at the end of each financial year.
- Minimum Balance: You must maintain a minimum balance of Rs. 500 in your Post Office Savings Account, making it accessible to individuals with varying income levels.
- Withdrawals: The minimum withdrawal allowed is Rs. 50, and withdrawal will not be allowed in case of a low balance that is lower than the minimum balance threshold of Rs. 500
- Nomination: Nomination is mandatory and must be nominated when opening the Account.
- Transferability: The Account can be transferred from one post office to another.
- Tax Exemption: Interest earned from a savings account up to Rs. 10,000 in a Financial Year is exempted from taxable Income.
- Facility: A Cheque facility/ATM facility can be availed.
How to Open a Post Office Savings Account:
- Visit the Nearest Post Office: Individuals must visit their nearest branch to open a Post Office Savings Account.
- Fill out the Application Form: Fill out the required application form, providing personal details such as name, address, and nominee information.
- Submit Identity and Address Proof: Submit the necessary identity and address proof documents and passport-sized photographs.
- Deposit the Initial Amount: Deposit the initial amount required to open the Account. The minimum deposit amount may vary.
- Receive the Passbook: Once the Account is opened, the account holder is provided with a passbook, which serves as a record of transactions and reflects the account balance.
2) Post Office Recurring Deposit
Post office RD accounts allow individuals to save a fixed amount of money every month for 5 years, which can be further extended to another 5 years by applying at the concerned Post Office. The government sets interest rates generally higher than those offered by regular savings accounts.
- Flexible Monthly Deposits: Investors can make monthly contributions,
- Fixed Tenure Options: The Recurring Deposit offers fixed tenure for 5 years (60 monthly deposits) from the opening date, with an option to extend for a further 5 years, providing a structured approach to savings.
- Interest Rate: The government sets the interest rates with quarterly compounding and are usually competitive, ensuring a reasonable return on investment.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: A minimum of INR 100/- per month or any multiple of INR 10/- is required to open a Post Office Recurring Deposit. There is no upper limit on the amount that can be deposited monthly, giving individuals the freedom to save as per their financial capacity.
- Nomination Facility: Investors can nominate a family member to receive the maturity amount in case of unforeseen circumstances, adding a layer of financial security.
- Premature Withdrawal: While premature withdrawals are allowed upon completion of 3 years from the date of account opening, however
- Interest Compounding: Interest is compounded quarterly or as per the terms, contributing to the overall growth of the investment.
- Tax Benefits: The interest earned on the Post Office Recurring Deposit is taxable but is eligible for tax deduction under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
- Accessibility: Being a government-backed savings scheme, the Post Office Recurring Deposit is accessible to individuals across various income groups and geographical locations.
- Transferability: In relocation, investors can transfer their Recurring Deposit account from one post office to another, ensuring continuity in savings.
- Loan Facility: Investors can avail themselves of loans against their Recurring Deposit after a certain period, providing a financial cushion in times of need.
- Senior Citizen Benefits: Special provisions may exist for senior citizens, offering them potentially higher interest rates and other advantages.
3) Post Office Fixed Deposit / Time Deposit (TD)
Post office fixed deposits, known as Time Deposit (TD), offer deposits for various tenures, starting from 1 year, 2 years, 3 years, and 5 years. The government sets the interest rates on these fixed deposits, typically higher than savings Account rates.
Here are some key features of Post Office Time Deposit:
- Fixed Tenure: Post Office Term Deposit comes with fixed tenures, typically ranging from 1 year to 5 years. Investors can choose the duration based on their financial goals and requirements.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: A minimum deposit of Rs. 1,000 is required to open a Post Office Time Deposit, and investors can deposit amounts in multiples of Rs. 100. There is also usually no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Interest Rates: The government sets the interest rates for Post Office Time Deposits, which are usually higher than regular savings accounts. The rates may vary based on the tenure of the deposit.
- Interest Payment: The interest on Post Office Time Deposits is usually compounded quarterly and paid out annually; this means that the interest earned in the previous quarters is added to the principal, and the new interest is calculated on the updated amount.
- Premature Withdrawal: While Post Office Time Deposits are designed for a fixed tenure, premature withdrawal is allowed under certain conditions. However, there will be a reduction in the interest rate for such withdrawals.
- Tax Benefits: The interest earned on Post Office Time Deposits is taxable. However, under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act in some countries, the principal amount is eligible for tax deductions.
- Renewal Option: Investors can renew their Post Office Time Deposit account for another term at the prevailing interest rates.
- Nomination Facility: Investors can nominate a person to receive the maturity amount in case of their demise during the tenure of the deposit.
Documents Required to Open Post Office FD
- Application Form: Most post offices provide a specific application form for opening a Fixed Deposit account. This form requires details such as the investor’s name, address, contact information, and deposit amount.
- Identity Proof: A valid government-issued identity proof is essential. Commonly accepted identity proofs include:
- Passport
- Voter ID card
- Aadhaar card
- Driving license
- Address Proof: Proof of residence is required to verify the investor’s address. Acceptable address proofs include:
- Utility bills (electricity, water, gas)
- Rental agreement
- Bank statement
- Aadhaar card (if it has the address mentioned)
- Photographs: Passport-sized photographs of the investor are usually required for documentation.
- PAN Card: In many countries, providing a Permanent Account Number (PAN) card is mandatory for opening a Fixed Deposit account. This is especially important for tax purposes.
- Income Proof: Some post offices may require proof of Income, especially for larger deposit amounts. This could include salary slips, income tax returns, or other income-related documents.
4) Monthly Income Scheme (MIS)
The Monthly Income Scheme is a post office savings scheme that offers monthly interest payments. It is suitable for individuals looking for a regular source of Income. The tenure of an MIS account is 5 years.
Here are some key features of a Monthly Income Scheme:
- Investment Duration: MIS typically comes with a fixed investment duration. Investors commit a lump sum amount for a specified period, often ranging from 5 to 10 years.
- Regular Income: One of the primary features of MIS is that it provides a regular and stable monthly income to investors. This can be particularly attractive for individuals seeking a consistent cash flow.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates for MIS are generally predetermined, revised quarterly, and paid out monthly.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: MIS account can be opened with a minimum of Rs.1,000 and in multiples of Rs.1,000 with a maximum investment of Rs. 9 lakh for a single account and 15 lakh in a joint account.
- Premature Withdrawal: While MIS is designed for a fixed term, there may be provisions for premature withdrawal under certain circumstances. However, withdrawal within 1 year is not allowed, and after 1 year, such premature withdrawals are subject to a predefined percentage reduction in the principal.
- Tax Implications: The interest earned through MIS is taxable.
- Nomination Facility: Like other financial instruments, MIS typically allows investors to nominate a beneficiary who would receive the investment in the event of the investor’s demise.
5) Public Provident Fund (PPF)
PPF is a long-term savings scheme with a tenure of 15 years, which can be extended in blocks of 5 years. It offers tax benefits and competitive interest rates. Deposits made in a PPF account are also eligible for deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act.
Here are the key features of the Public Provident Fund:
- Eligibility: PPF is open to all residents, including salaried individuals, self-employed individuals, and even minors. Non-resident Indians (NRIs) are not eligible to open a new PPF account, but existing accounts can be continued until maturity.
- Investment Duration: The PPF comes with a fixed term of 15 years. However, investors have the option to extend the tenure in blocks of 5 years each after the initial maturity.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate for PPF is set by the government and is subject to periodic revisions. The interest is compounded annually. The rates are typically higher than those offered by regular savings accounts.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: Investors can open a PPF account with a minimum deposit amount of Rs. 500, and can contribute to the account in multiples of Rs. 50. There is also a maximum investment limit of Rs. 1.5 lakhs per annum, either made in installment or lump sum.
- Tax Benefits: Contributions made to the PPF account, interest earned, and the maturity amount are all eligible for tax benefits under specific sections of the Income Tax Act. The interest earned is tax-free, and the contribution qualifies for deductions.
- Withdrawal: While the PPF has a lock-in period of 15 years, partial withdrawals are allowed from the 7th year onwards. However, there are limits on the amount that can be withdrawn (Maximum 50% of the balance), and premature closure is generally not allowed.
- Loan Facility: PPF account holders can avail of loans against their PPF deposits from the 3rd year up to the 6th year. The interest on such loans is typically lower than other forms of borrowing.
- Nomination Facility: PPF allows investors to nominate a person who would receive the maturity amount in case of the account holder’s demise.
- Transferability: Individuals can transfer their PPF account from one authorized bank or post office to another at their convenience.
- Extension of Maturity: At the end of the initial 15-year term, investors can extend the PPF account in blocks of 5 years each, allowing for continued tax-free compounding.
- Accessibility: PPF accounts can be opened at authorized banks and post offices, making them widely accessible to individuals across urban and rural areas.
- Security: PPF is considered a safe investment as it is backed by the government, providing assurance regarding the safety of the principal amount.
6) Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS)
SCSS is a dedicated investment option for senior citizens and offers a higher interest rate than other post office schemes. The maturity period for SCSS is 5 years and can be extended once for an additional 3 years.
Here are some key features of the Senior Citizens Savings Scheme:
- Eligibility: As the name suggests, the SCSS is exclusively designed for senior citizens. The eligibility age is usually 60 years or above.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: Investors can invest in SCSS with a minimum deposit of Rs.1,000 and in multiples of 1,000, subject to a maximum limit of up to Rs. 30 lakh for each individual.
- Investment Duration: The SCSS comes with a fixed tenure, typically 5 years, which can be extended for an additional 3 years after maturity; this allows senior citizens to choose a longer investment horizon if they wish.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates for the Senior Citizens Savings Scheme are set by the government and are generally higher than those offered on regular savings accounts. The rates get revised quarterly.
- Interest Payment: Interest is usually paid out quarterly, providing a regular income stream to senior citizens. The interest is directly credited to the investor’s bank account.
- Tax Benefits: The investment made in the SCSS is eligible for tax benefits under specific sections of the Income Tax Act. However, the interest earned is generally taxable.
- Premature Withdrawal: Premature withdrawal is allowed under certain conditions, although it may be subject to penalties.
- Renewal Option: After the initial 5-year tenure, investors have the option to extend the scheme for an additional 3 years. The extension is subject to the prevailing terms and conditions at the time of renewal.
- Nomination Facility: SCSS allows investors to nominate a beneficiary who would receive the investment in the event of the investor’s demise.
- Accessibility: The Senior Citizens Savings Scheme is commonly available at designated bank branches and post offices, making it accessible to senior citizens across both urban and rural areas.
- Security: SCSS is considered a safe investment as it is backed by the government. This gives senior citizens a sense of security regarding the return on their invested capital.
Senior Citizens Savings Scheme is a popular investment choice for retirees or those approaching retirement age due to its safety, regular income stream, and favorable interest rates. However, individuals should carefully review the specific terms and conditions of the scheme and seek professional advice if needed.
7) National Savings Certificate (NSC)
The Post Office National Savings Certificate (NSC) is a fixed-income savings scheme that encourages small and long-term savings among individuals.
Here are the key features of the Post Office National Savings Certificate:
- Investment Tenure: NSCs come with a fixed tenure of 5 years.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate for National Savings Certificates is set by the government and revised quarterly.
- Interest Calculation: Interest is compounded annually but is payable only at the time of maturity.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: Minimum investment required is Rs. 1,000 and in multiple of Rs. 100. There is usually no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Tax Benefits: The interest earned through National Savings Certificates is taxable, but the investment amount qualifies for deductions under section 80C of the Income Tax Act in India.
- Premature Withdrawal: While NSCs are designed for a fixed tenure, premature withdrawal is allowed only in case of death of account holder, on forfeiture by a pledgee being a Gazetted officer or on order by court.
- Nomination Facility: NSCs typically allow investors to nominate a person who would receive the maturity amount in case of the investor’s demise.
It’s crucial for individuals considering National Savings Certificates to review the specific terms and conditions of the scheme.
8) Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP)
The Post Office Kisan Vikas Patra (KVP) is a savings scheme offered by the post office, primarily designed to encourage long-term savings among farmers and individuals in rural areas. KVP doubles the investment amount after a specified period (usually 115 months). Someone looking to double their money in the long run with safety can opt for KVP.
Here are the key features of the Post Office Kisan Vikas Patra:
- Investment Tenure: Kisan Vikas Patra comes with a fixed tenure, and the investment matures after a predetermined period. The tenure for KVP is typically 115 months (9 years & 7 months).
- Interest Rate: The interest rate for Kisan Vikas Patra is set by the government and revised quarterly.
- Interest Calculation: The interest is compounded annually, but it is payable only at the time of maturity.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: Kisan Vikas Patra can be purchased for a minimum amount of Rs. 1,000 and in multiple of Rs. 100 with no upper limit on the investment amount.
- Tax Implications: The interest earned through Kisan Vikas Patra is taxable. However, the investment amount itself does not qualify for any tax benefits. Investors should be aware of the tax implications and factor them into their financial planning.
- Nomination Facility: KVP provides the option for investors to nominate a person who would receive the maturity amount in case of the investor’s demise.
- Premature Withdrawal: While KVP is designed for a fixed tenure, premature withdrawal is allowed under certain conditions. However, the amount withdrawn prematurely may be subject to penalties, and the interest rate applicable could be lower.
9) Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana (SSY)
SSY is a government-backed savings scheme to benefit the girl children. Parents or legal guardians can open an account in the name of a girl child and contribute until she reaches 21. Here is the detailed article on Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana.
- Account Opening: The Account can be opened in the name of a girl child by her parent or guardian before the child turns 10 years old. One family can open one Account for each girl child and up to two accounts. However, in the case of twins/triplets, girls birth more than two accounts can be opened.
- Minimum and Maximum Investment Limit: The minimum deposit amount required to open an account is Rs. 250, and the maximum deposit amount allowed per annum is Rs. 1.5 lakh (in multiple of Rs.50).
- Frequency of deposit: Lumpsum or multiple, the total deposit in a financial year should not exceed Rs. 1.5 lakhs.
- Maturity Tenure: The Account matures on the completion of 21 years from the account opening date. Many need clarification about whether it’s 21 years of the child or 21 years from the account opening. It is suggested to open the SSY account immediately on the birth of a girl child; that is why it is assumed that the Account matures when the girl child attains 21 years, and that’s why the confusion. I hope this clarifies your doubts.
- Premature account closure: Premature account closure is allowed after 5 years of account opening under certain circumstances, such as
- On the death of the account holder
- On medical grounds
- On the death of the guardian by whom the Account operated
- Interest Rate: The interest rate on the deposits is fixed by the government every quarter. The current interest rate is 8% per annum (with effect from 01-04-2023 ), compounded annually. Interest gets credited to the Account at the end of each Financial year. The interest rate is higher than most other savings schemes, making it an attractive investment option.
- Tax Benefits: The deposits made in the scheme are eligible for tax benefits under section (u/s) 80C of the Income Tax Act. The interest earned and the amount withdrawn on maturity are tax-free.
- Withdrawal: The amount deposited can be withdrawn on maturity or used for the girl child’s education or marriage. Up to 50% of the balance can be withdrawn after the girl child turns 18, provided she is pursuing higher education. The balance is paid to the nominee in case of the account holder’s death.
- Closure on maturity:
- After completing 21 years from the Account’s opening date.
- At the time of marriage of the girl child after attaining the age of 18 years.
Documents Required for Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana account opening form.
- The birth certificate of the girl child.
- The ID proof and address proof of the depositor.
- A medical certificate is needed if multiple children are born under one birth order.
- Any other documents that the bank or post office requests.
Conclusion
You must carefully introduce debt into your goal-based investing portfolio, and SSY is apt for girl child education/marriage goals, whereas 3 Year Time Deposit is for any goal of tenure of 3-4 years. Don’t hesitate contacting financial planning expert for your personal finance planning.





