With the income tax due date approaching, the assessee has become serious about filing an ITR; confusion continues how to file an ITR for capital gains. In this article, I will explain step by step with screenshots that will help you complete your ITR-2/ ITR-3 form capital gain section.
What is ITR for Capital Gains?
ITR for Capital Gains refers to the Income Tax Return filed by an individual or business professional that has earned capital gains from the sale of a capital asset. It is a mandatory requirement by the Income Tax Department for individuals or businesses that have booked long-term capital gains or short-term capital gains above the basic exemption limit.
Filing ITR for Capital Gains is essential for individuals, businesses, or professions to comply with the Income Tax Act 1961 and avoid legal consequences.

Importance of ITR for Capital Gains
Filing ITR for Capital Gains is crucial for salaried individuals or business professionals to establish financial credibility and avoid legal consequences. It is also essential for claiming tax refunds and avoiding penalties.
Benefits of Filing ITR for Capital Gains
Claiming Tax Refunds
Filing ITR for Capital Gains allows salaried individuals, businesses, or professionals to claim Tax refunds if they have paid more tax than their actual tax liability. To claim a tax refund, you must file your ITR on time, and for FY 2023-24, the due/last date for filing your ITR is 31 July 2024.
Avoiding Penalties
Filing ITR for Capital Gains is mandatory for salaried individuals or business professionals who have booked long-term or short-term capital gains above the basic exemption limit. Failure to file ITR for Capital Gains can attract penalties and legal consequences.
| Penalty Type | Penalty Under Section | Max Penalty |
|---|---|---|
| Interest | 234A | Interest at a rate of 1% per month |
| Late fee | 234F | Income below 5 Lakhs: Rs.1,000 Income above 5 Lakhs: – Filing After 31st July until 31st Dec: Rs. 5,000 – Filing After 31st Dec until 31st March: Rs. 10,000 |
Establishing Financial Credibility
Filing ITR for Capital Gains is essential for salaried individuals or business professionals to establish financial credibility. It helps obtain loans, credit cards, and other financial products from banks and financial institutions.
Implications of Not Filing ITR for Capital Gains
Legal Consequences
Not filing an ITR for Capital Gains can attract legal consequences, including penalties and prosecution. It is essential to file ITR for Capital Gains to comply with the Income Tax Act of 1961 and avoid any legal repercussions.
Difficulty in Obtaining Loans
Not filing an ITR for Capital Gains can make it difficult for salaried individuals or business professionals to obtain loans. Filing an ITR for Capital Gains is essential to establishing financial credibility and getting financial products.
Loss of Financial Credibility
Not filing an ITR for Capital Gains can lead to a loss of financial credibility. It can affect the credit score and make it difficult for individuals or businesses to obtain financial products from banks and financial institutions.
Steps to File ITR for Capital Gains?
Understanding the Process
Filing ITR for Capital Gains involves the following steps:
- Determine the type of capital gain – long-term or short-term.
- Calculate the capital gain.
- Determine the tax liability.
- File ITR for Capital Gains using the ITR-2 form for salaried individuals and ITR-3 for business professionals.
Learn more: ITR 1 vs ITR 2 Form: Tax Return Filing Guide for Salaried Individual
Documents Required To File ITR-2 & ITR-3
The following documents are required to file ITR for Capital Gains:
- If you have sold Mutual Fund Units: A capital gain statement from a mutual fund. You can also run a consolidated capital gain statement from CAMS & Karvy.
Note: If you have set up STP or switched from one mutual fund scheme to another or from a regular plan to a direct plan and vice versa, then they are considered a sale of mutual fund units, and there will be capital gain or loss against these movements.
- If you have sold shares: A capital gain statement from the Demat account.
- If you have sold real estate property: Take a professional’s help to calculate capital gain. They will need a sale deed or purchase deed of the capital asset.
How to Fill ITR Form ITR-2 / ITR-3 for Capital Gains
When filling out Capital gain forms, the same procedure applies to both forms, ITR-2 / ITR-3 (the old and new tax regimes).
⚠️Note: The screenshots below are for AY 2023-24. You must select the appropriate AY when filing.
To fill out the ITR form online, follow these steps:
- Log into the IT Department e-filing portal using the below link.
https://eportal.incometax.gov.in/iec/foservices/#/login
- Click the button “File Now.”
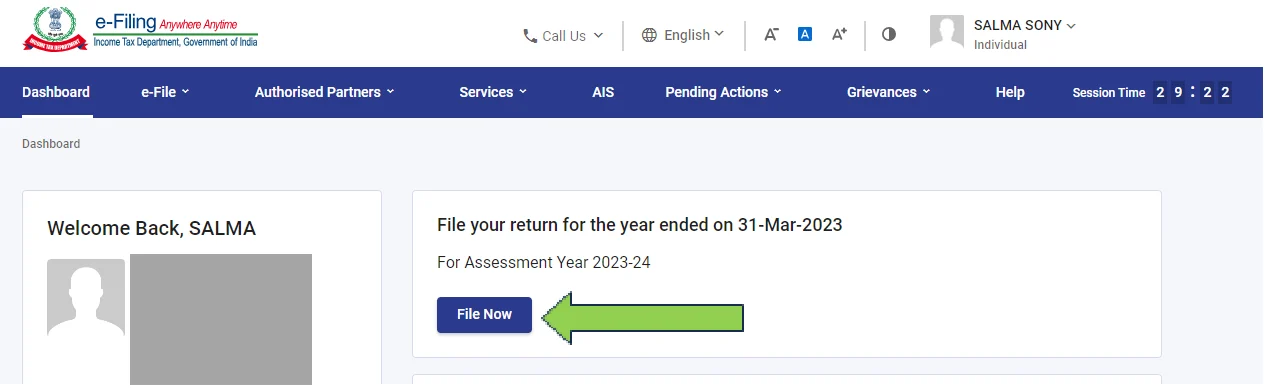
- Select the appropriate assessment year and mode of filing “Online,” then continue.
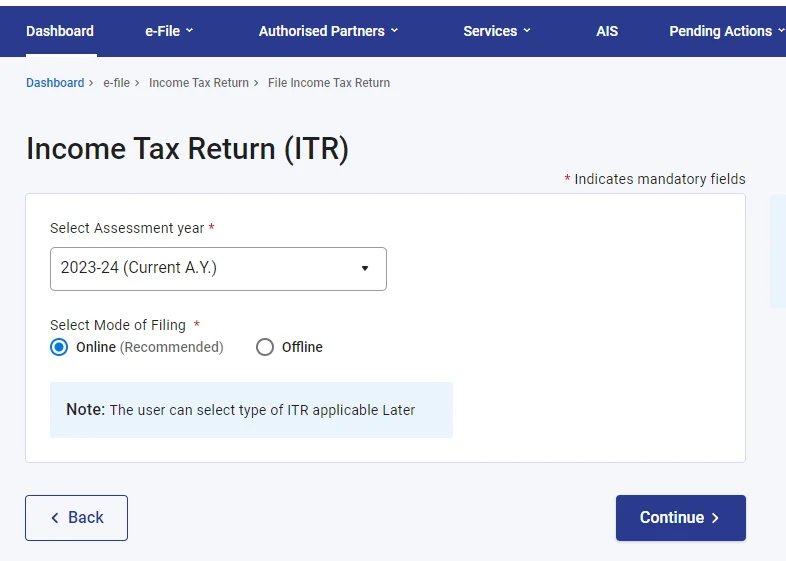
- Now click on “Start new filing.“
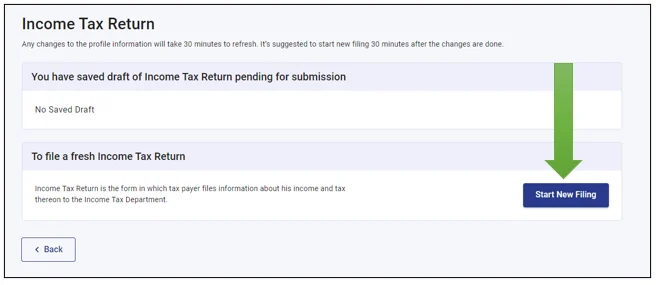
- Select an “Individual” and continue.
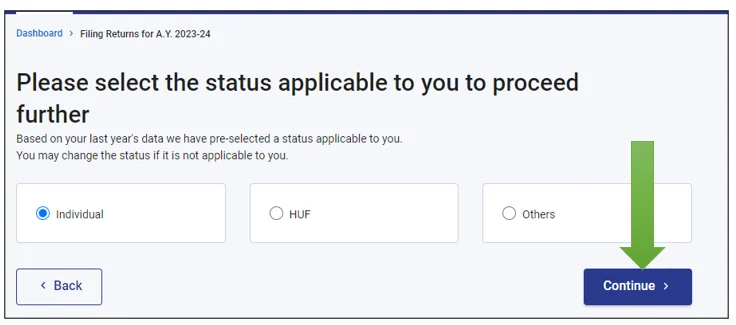
- Choose the appropriate ITR Form & proceed. I am selecting ITR-2 and proceeding.
- As mentioned, the capital gain form is the same in ITR-2 & ITR-3.
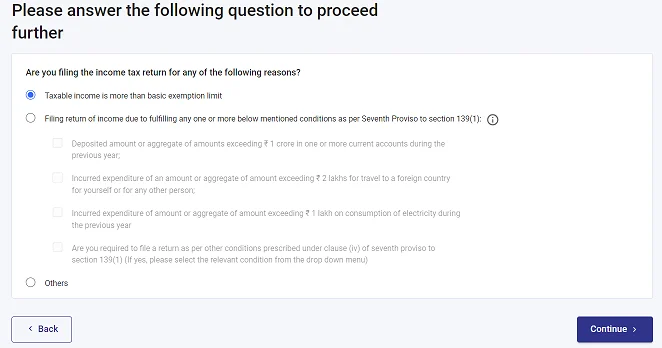
- Opt for the option applicable to you and proceed. I am selecting “Taxable income more than basic exemption” and proceeding.
- Here, you need to select “Scheduled Capital Gains.“
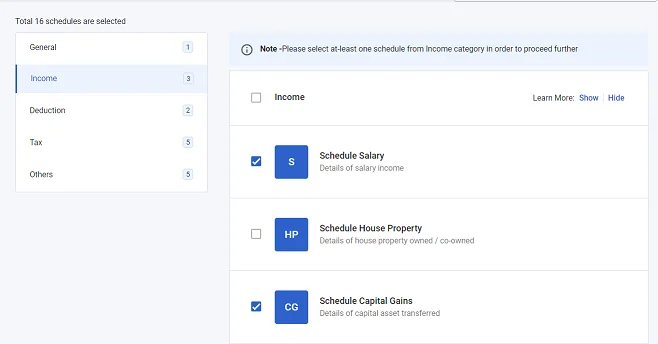
Step-1
Having Capital gain income from equity mutual funds or shares, checkmark the option below and proceed.
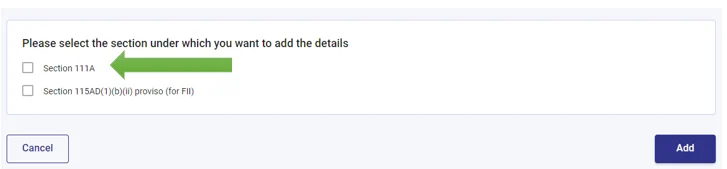
- Section 111A – Short-term capital gain
- Section 112A – Long-term capital gain
Having Capital gain income from debt mutual funds, checkmark the below option.
- From the sale of assets other than all the above-listed items
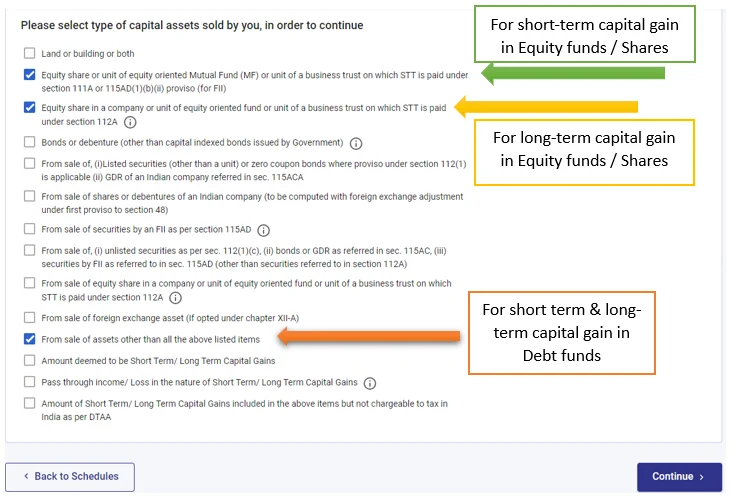
Step-2
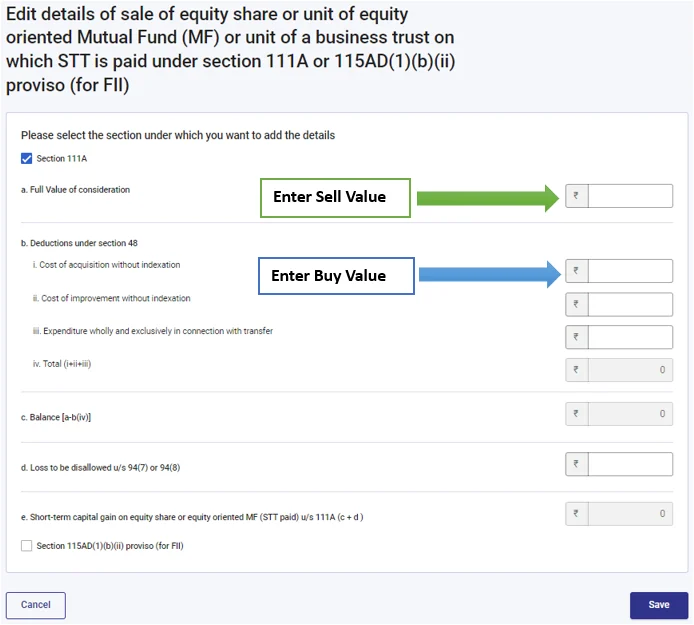
A) For Equity Short-term Capital Gain
Select, Equity share or unit of equity oriented Mutual Fund (MF) or unit of a business trust on which STT is paid under section 111A or 115AD(1)(b)(ii) proviso (for FII)
- Add details
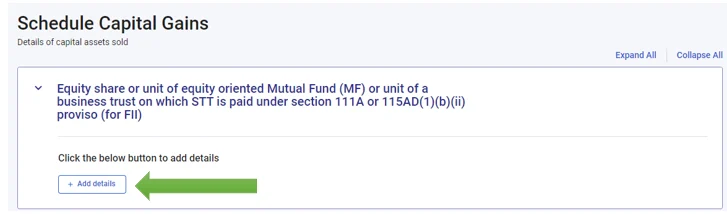
- Select 111A
- Fill buy and sell value as shown in the below screenshot.
B) For Equity Long-term Capital Gain
Select, Equity share in a company or unit of an equity-oriented fund or unit of a business trust on which STT is paid under section 112A
- Add details
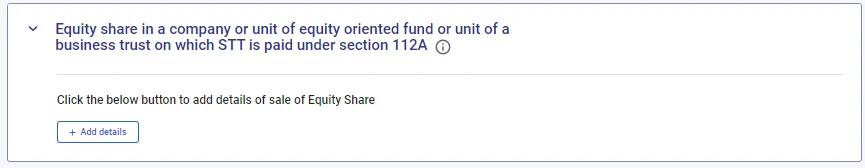
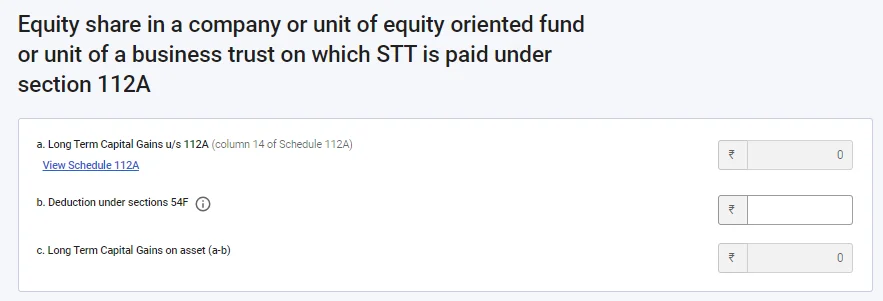
- Click on “view schedule 112A.“
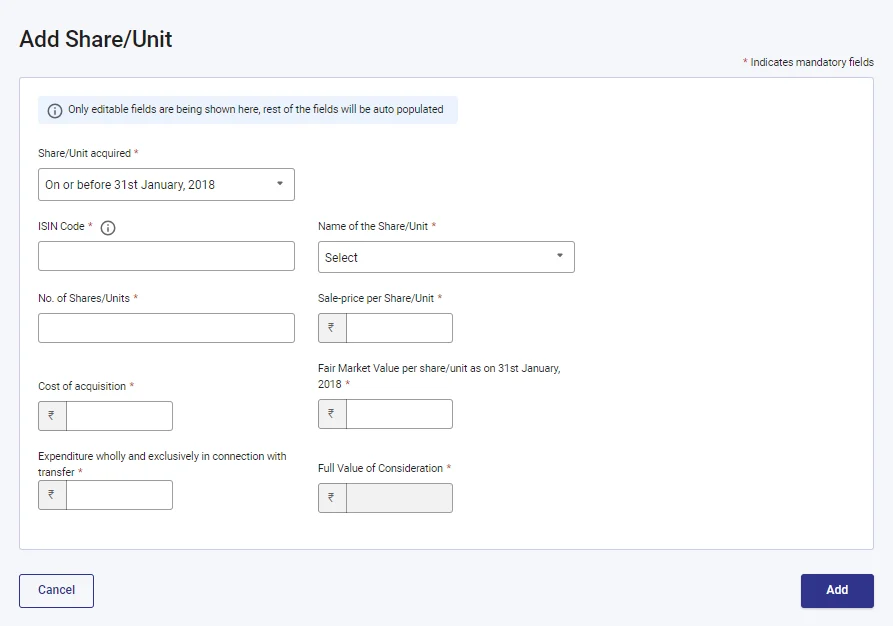
If the purchase date of sale of units/shares is on or before 31st January 201, then add the below details:
- Share/Unit acquired
- ISIN Code
- No. of Shares/Units
- Sale price per Share/Unit
- Cost of acquisition
- Fair Market Value per share/unit as on 31 January, 2018
- Expenditure wholly and exclusively in connection with transfer
- Full Value of Consideration
If the purchase date of sale of units/shares is after 31st January 2018, then add the below details:
- Cost of acquisition
- Expenditure wholly and exclusively in connection with transfer (Example- STT paid)
- Full Value of Consideration
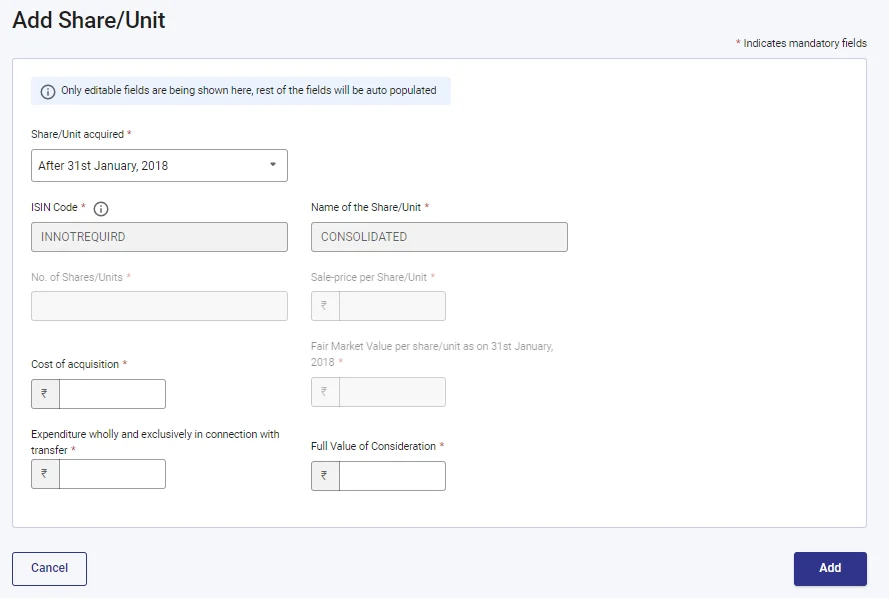
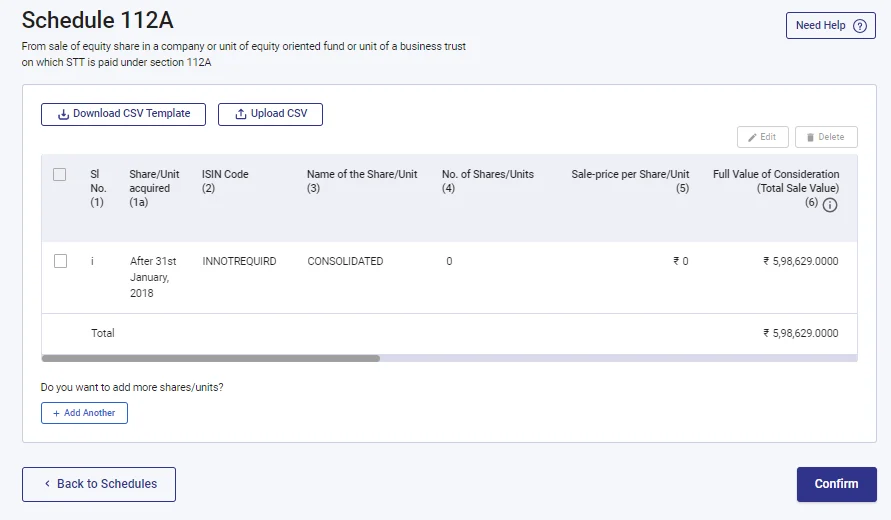
- After adding details, this is how it will look, then confirm
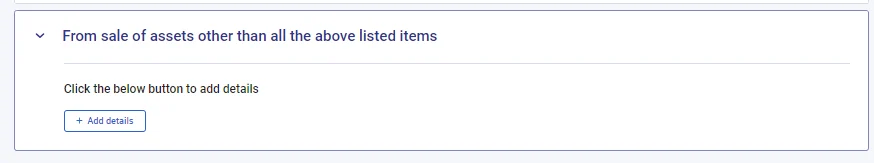
C) For Debt Funds Short-term & Long-term Capital Gain
Select “From sale of assets other than all the above-listed items.“

- Add details
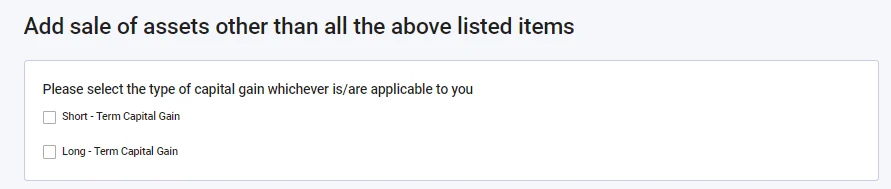
- Select Short-term capital gain, or Long-term capital gain, or both, whichever is applicable.
- If you selected short-term capital gain, fill in the “buy value” and “sell value” as shown in the screenshot below.
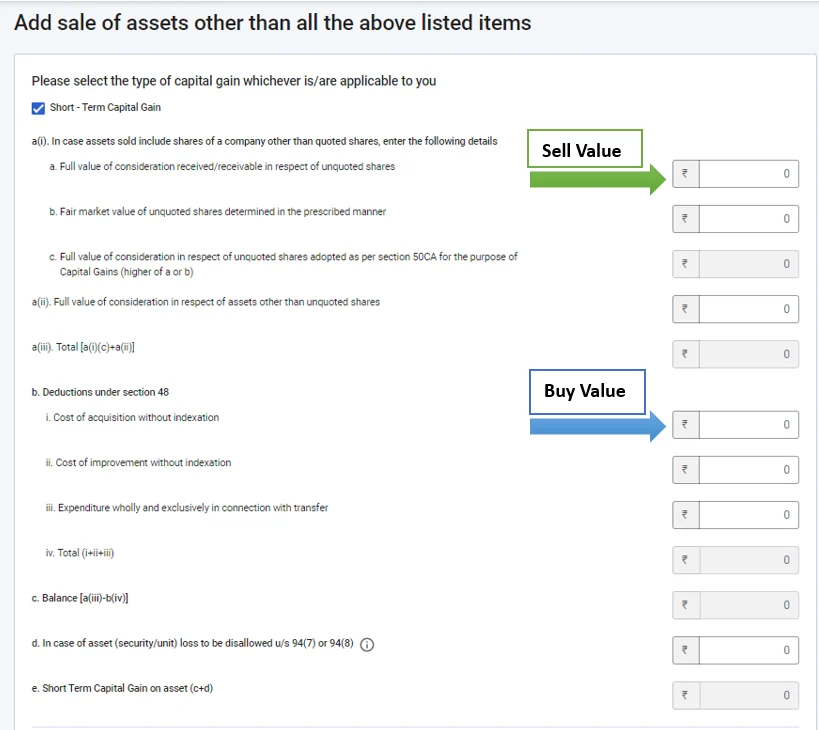
- If you have selected long-term capital gain, fill in the buy and sell value shown in the screenshot below.
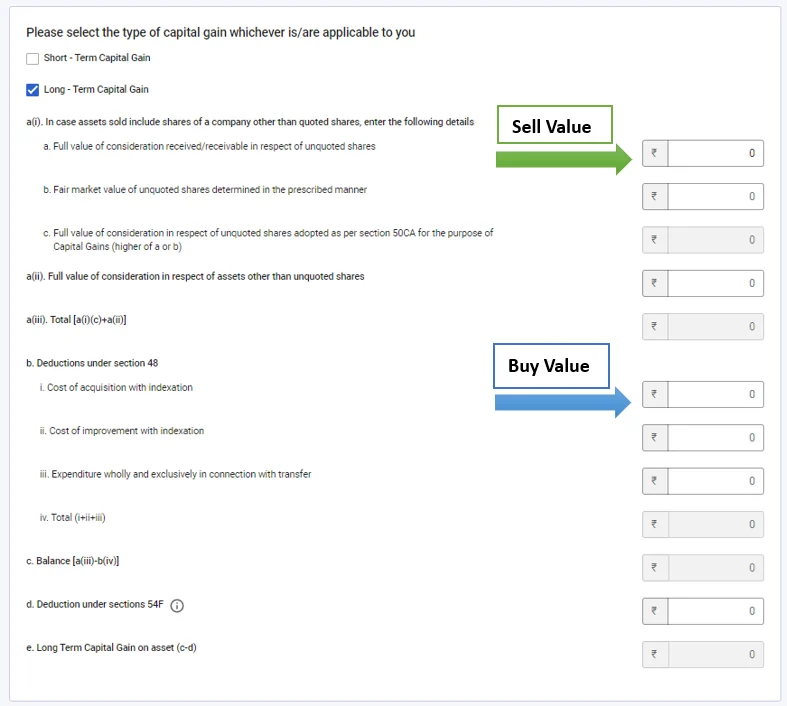
Now, here is the tricky part. Here you need to refer to the capital gain statement and enter the break-up of the capital gain.
Example: Assume you have an equity short-term capital gain of Rs. 10,000 this financial year. By referring capital gain report, you will get the data on the month of sale of units/shares.
You need to segregate the capital gain in the below date slot and enter the details accordingly
1st April – 15th June | Rs. 2,500
16th June – 15th Sep | Rs. 3,500
16th Sep – 15th Dec | Rs. 2,000
16th Dec – 15th March | NIL
16th March – 31st Dec | Rs. 2,500
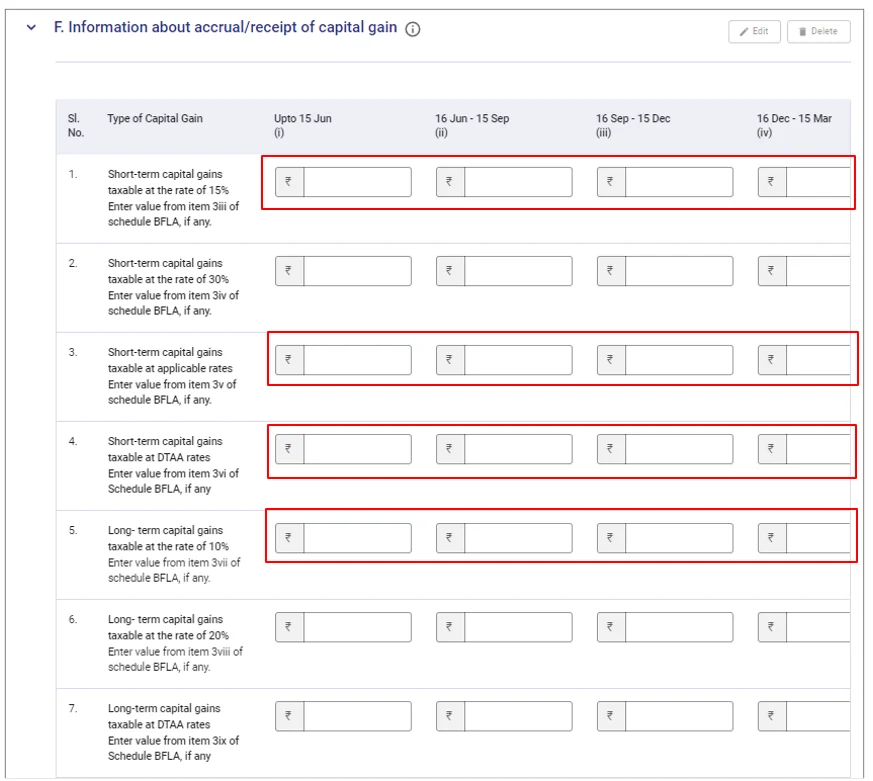
Note: The addition of segregation should add up to Rs. 10,000 in this example. In case there is a difference of even Re. 1, then an error will be shown and won’t allow to proceed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
The following are common mistakes to avoid while filing ITR for Capital Gains:
- Reporting only some capital gains.
- Not claiming tax deductions.
- Do not refer to form-26 AS & AIS report
- Not verifying the ITR.
Conclusion
In conclusion, filing ITR for Capital Gains is essential for salaried individuals or business professionals to comply with the Income Tax Act of 1961 and avoid legal consequences. If you find the entire process hectic, don’t hesitate to get professional advice to file your capital gains correctly through ITR.
It is recommended that you focus on tax planning at the beginning rather than the end of the financial year. A good way to do this is to focus on financial planning, which also includes tax planning. This will help you achieve your financial goals on time and live a peaceful financial life.
Related Income Tax Articles
Maximize Your Tax Savings With Tax Harvesting Mutual Funds
18 Common Tax Filing Mistakes You Must Avoid FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24)
ITR For Salaried Person: Which ITR Should I File For FY 2022-23 (AY 2023-24)?
Tax Planning For Salaried Employees





